Reaction data
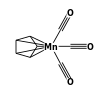 (solution) +
(solution) + 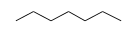 (solution) = C14H21MnO2 (solution) +
(solution) = C14H21MnO2 (solution) + 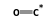 (solution)
(solution)
- Reaction by formula: C8H5MnO3 (solution) + C7H16 (solution) = C14H21MnO2 (solution) + CO (solution)
- Information on this page:
- Other data available:
- Options:
Enthalpy of reaction at standard conditions (nominally 298.15 K, 1 atm.)
Go To: Top, References, Notes
Data compilation copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the U.S.A. All rights reserved.
Data compiled by: José A. Martinho Simões
| ΔrH° (kcal/mol) | Method | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 46.9 ± 1.8 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by HeSiH3. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 48.3 ± 1.2 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by Me2EtSiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.7 ± 2.1 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by Et3SiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.5 ± 2.0 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by Pr3SiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 45.6 ± 3.0 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by He3SiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.5 ± 1.8 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by (i-Bu)3SiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 47.2 ± 1.7 | PAC | Hester, Sun, et al., 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by (i-Pr)3SiH. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.7 ± 1.1 | PAC | Yang and Yang, 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by CH2Cl2. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 47.11 ± 0.91 | PAC | Yang and Yang, 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by CH2Br2. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.9 ± 1.0 | PAC | Yang and Yang, 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by BuCl. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.7 ± 1.0 | PAC | Yang and Yang, 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by BuBr. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.61 ± 0.60 | PAC | Yang and Yang, 1992 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by PeBr. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 47.8 ± 4.1 | PAC | Johnson, Popov, et al., 1991 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation.; MS |
| 44.7 ± 1.4 | PAC | Burkey, 1990 | solvent: Heptane; The enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 46.2 ± 1.2 | PAC | Klassen, Selke, et al., 1990 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by thf. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 47.8 ± 1.7 | PAC | Klassen, Selke, et al., 1990 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by Me2CO. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 47.6 ± 1.4 | PAC | Klassen, Selke, et al., 1990 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by cis-cy-C8H14. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
| 45.3 ± 1.4 | PAC | Klassen, Selke, et al., 1990 | solvent: Heptane; The reaction is the first of two consecutive reactions, the second being the replacement of heptane by Bu2S. The reaction enthalpy relies on 0.65 for the quantum yield of CO dissociation; MS |
References
Go To: Top, Enthalpy of reaction at standard conditions (nominally 298.15 K, 1 atm.), Notes
Data compilation copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the U.S.A. All rights reserved.
Hester, Sun, et al., 1992
Hester, D.M.; Sun, J.; Harper, A.W.; Yang, G.K.,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 5234. [all data]
Yang and Yang, 1992
Yang, P.-F.; Yang, K.G.,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 6937. [all data]
Johnson, Popov, et al., 1991
Johnson, F.P.A.; Popov, V.K.; George, M.W.; Bagratashvili, V.N.; Poliakoff, M.; Turner, J.J.,
Mendeleev Commun., 1991, 145.. [all data]
Burkey, 1990
Burkey, T.J.,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 8329. [all data]
Klassen, Selke, et al., 1990
Klassen, J.K.; Selke, M.; Sorensen, A.A.; Yang, G.K.,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 1267. [all data]
Notes
Go To: Top, Enthalpy of reaction at standard conditions (nominally 298.15 K, 1 atm.), References
- Symbols used in this document:
ΔrH° Enthalpy of reaction at standard conditions - Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69: NIST Chemistry WebBook
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of the Database and to verify that the data contained therein have been selected on the basis of sound scientific judgment. However, NIST makes no warranties to that effect, and NIST shall not be liable for any damage that may result from errors or omissions in the Database.
- Customer support for NIST Standard Reference Data products.